brinell hardness test ball material|brinell hardness test calculator : retailer Sintered carbide balls with a standardized diameter of 10 mm, 5 mm, 2.5 mm, 2 mm or 1 mm are available as test balls for Brinell hardness testing. Small diameters are necessary for thinner sheets, as balls that are too . Contactme Branco - Contactme | O futuro digital do seu cartã.
{plog:ftitle_list}
For a while now, you’ve been able to use XML-format .ytyp/.y.
The Brinell hardness test is commonly used to determine the hardness of materials . Sintered carbide balls with a standardized diameter of 10 mm, 5 mm, 2.5 mm, 2 mm or 1 mm are available as test balls for Brinell hardness testing. Small diameters are necessary for thinner sheets, as balls that are too .The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 kN; 6,614 lbf) force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: where:Brinell hardness is a unit of measurement that indicates the hardness of a material. It is measured using the Brinell hardness method, for which a hardmetal ball is pressed into the material. The size of the resulting indentation is .
The Brinell hardness lab test method consists of indenting the test material with a 10-mm-diameter hardened steel or carbide ball subjected to a load of 3000 kg. For softer materials, .When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested. The diameter of the .Learn how to use Brinell hardness test units and testing machines to quickly and accurately assess large samples with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure – with knowledge and insight from Struers, the world’s leading .The standard ball for Brinell testing is 10 mm (±0.005 mm) in diameter and should have a minimum hardness of 850 HV. When balls of smaller size are used, the load as well as the ball .
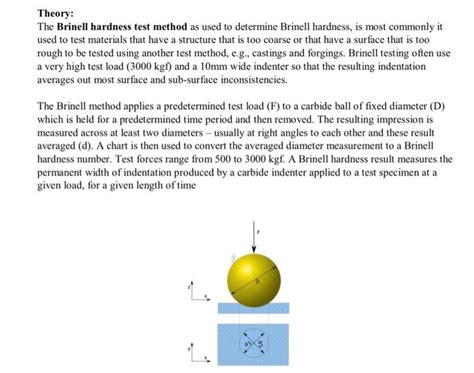
The Brinell method can be used for testing non-homogeneous materials (e.g. castings), because the large ball comes into contact with many crystals (different metallographic constituents of .Learrn more about hardness testing basics here. The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .
Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. . For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the . In the standard method of the Brinell Hardness Test, we use 250 to 500 kg of load for soft material and 500 to 3000 kg of load for hard material such as steel and iron. In the standard method of the test, we use a ball indenter of 10mm diameter.When is the Brinell hardness test used? Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested.
Hardness testing within the realm of materials testing. Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion .The oldest of the hardness test methods in common use on engineering materials today is the Brinell hardness test. Dr. J. A. Brinell invented this test in Sweden in 1900. . and thin stock are frequently tested using a 500 kg test force and a 10 or 5 mm ball. In Europe Brinell testing is done using a much wider range of forces and ball sizes .Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell hardness test is named after its inventor, Johan August Brinell. It involves applying a constant load or force to a spherical indenter made of hardened steel or carbide onto the surface of the material being tested. The indentation diameter is then measured optically.The test provides numerical results to quantify the hardness of a material, which is expressed by the Brinell hardness number – HB. The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten .
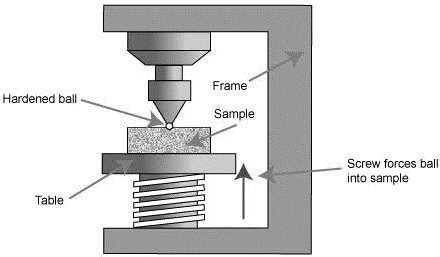
brinell hardness tester diagram
Choose an indenter, typically a hardened steel ball, with a diameter suited for the material and load being used. The standard ball sizes range from 1 mm to 10 mm. . Application of Brinell Hardness Test in Various Industries. The Brinell Hardness Test finds extensive application across diverse industries, playing a crucial role in assessing .Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation E10; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original . 5.2.3 Indenters—Indenters for the Brinell hardness test shall be tungsten carbide balls of four allowed diameters (1, 2.5, 5 and 10 mm). Indenters shall meet the .The Brinell hardness testing method is used in various cases where large or rough surfaces, coarse-grained materials, or high loads are involved. . The result of a Brinell method depends on the tested material, force, ball size and dwell time. An inden-tation is measured using a magnifying lens. The larger the measured diagonals, the softer .ISO 6506-3:2014, Metallic materials — Brinell hardness test — Part 3: Calibration of reference blocks ISO 6506-4, Metallic materials — Brinell hardness test — Part 4: Table of hardness values 3 Principle An indenter (tungsten carbide composite ball with diameter, D) is forced into the surface of a test piece
.Swedish metallurgist who devised the Brinell hardness test, a rapid, nondestructive means of determining the hardness of metals. Read More; materials testing. In materials testing: Hardness testing .a hardened steel ball (Brinell test) or a steel or diamond cone (Rockwell test) into the surface of the test piece. Most hardness tests are .
Brinell hardness test is one of the indentation hardness tests developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. . A smaller force is .
The Brinell hardness test. The Brinell hardness test is used for hardness testing larger samples in materials with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure. The Brinell hardness test (HBW) indentation leaves a relatively large impression, using a tungsten carbide ball. The size of the indent is read optically.Choose an indenter, typically a hardened steel ball, with a diameter suited for the material and load being used. The standard ball sizes range from 1 mm to 10 mm. 3. Test Machine Setup. . Advantages and Limitations of the Brinell .
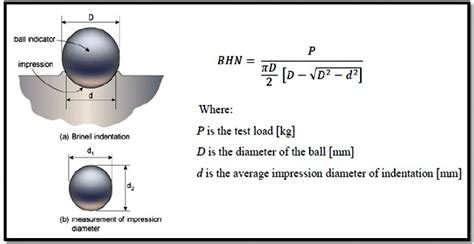
Brinell hardness test is most commonly used to test materials that have a structure that is too rough or too coarse to be tested using other test methods, e.g., castings and forgings. . the eye piece of the reading microscope may be turned up by 90 degree so that the impressions of the ball can be measured in two perpendicular directions .Brinell Hardness Testing Equation. Table A Brinell Hardness to Rockwell Hardness Conversion Table . Brinell Hardness: . Tensile Strength (Approximate) Psi: Tungsten Carbide Ball 3000 KG: A Scale 60KG: B Scale 100KG: C Scale 150KG-85.6-68.0--85.3-67.5--85.0-67.0-767: 84.7-66.4-757: . Materials and Specifications Mechanical Tolerances Specs .
ASTM E384: This standard is for hardness testing on a micro-scale, and therefore includes the Vickers and Knoop hardness tests. ISO 6506: This standard mirrors ASTM E10, as it contains the standard method for measuring the Brinell hardness of metals. ISO 6507: This standard contains the details for the Vickers hardness test in metallic materials.
METHOD FOR BRINELL HARDNESS TEST FOR METALLIC MATERIALS ( Third Revision) 1 Scope This part of ISO 6506 specifies the method for the Brinell hardness test for metallic materials and is applicable up to the limit of 650 HBW. For specific materials and/or products, particular International Standards exist (i.e. ISO 4498-l). 2 Normative references
The Brinell hardness test is an optical testing method for samples with coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure. This is the best test method for achieving the bulk or macro-hardness of a material, particularly those materials with heterogeneous structures. . (2.5mm and 5mm ball) Brinell Test Machine Description. The Brinell Hardness Tester .The Brinell hardness test uses a ball indenter of diameter, D, which is pressed into the surface of the test piece using a prescribed force, F. The time for the initial application of the force is 2 s to 8 s, and the test force is maintained for 10 s to 15 s. . Metallic materials. Brinell hardness test. Test method: ASTM E10-18: Standard Test . 1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information .
Explanation: Brinell hardness test uses ball indenter. Its diameter is kept 1 mm for lower load 1 kgf. It is taken 10 mm for 500 kgf load. 7. Brinell hardness number is not a function of _____ . Aircraft Materials – Hardness testing – Brinell and Rockwell Hardness ; Testing of Materials Questions and Answers – Vickers Hardness Test ; The Brinell hardness test measures material hardness by determining the diameter of an indentation made by a hardened steel or carbide ball under a specific load. A load, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 kgf, is applied to the material’s surface for 10-15 seconds, allowing the ball to penetrate and create an indentation.
1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information .
orion af8 volumetric karl fischer titrator distributor
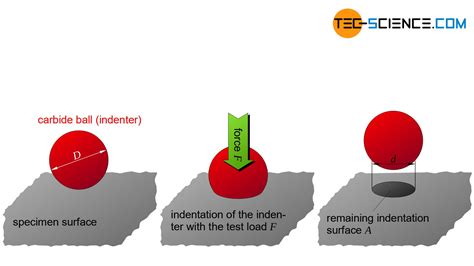
brinell hardness test theory
web2 de nov. de 2022 · Get the latest Football updates on Eurosport. Catch Shakhtar Donetsk - RB Leipzig live on 02/11/2022. Find scores, stats and comments in real time.
brinell hardness test ball material|brinell hardness test calculator